The Importance of Waterproofing in Elderly Fall Alert Devices

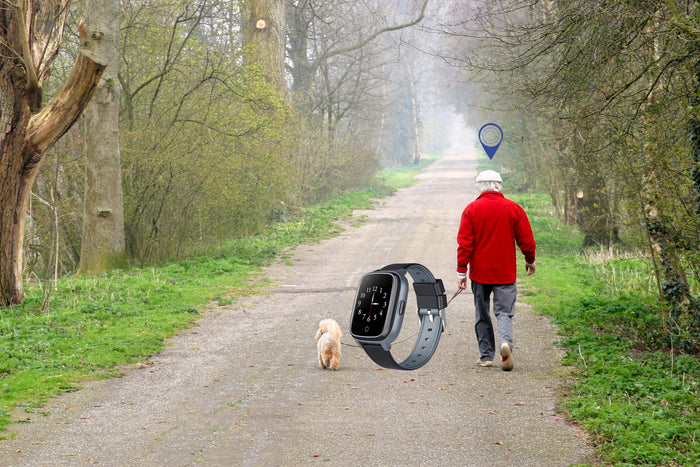
As the population ages, technology has become an essential ally in safeguarding the well-being of older adults. Fall alert devices, in particular, have emerged as lifesaving tools, allowing seniors to maintain their independence while providing peace of mind to their families. Among the many features of these devices, waterproofing is one of the most critical. This seemingly simple attribute plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability, usability, and effectiveness of fall alert devices, especially in environments where accidents are most likely to occur.
Protecting in High-Risk Areas
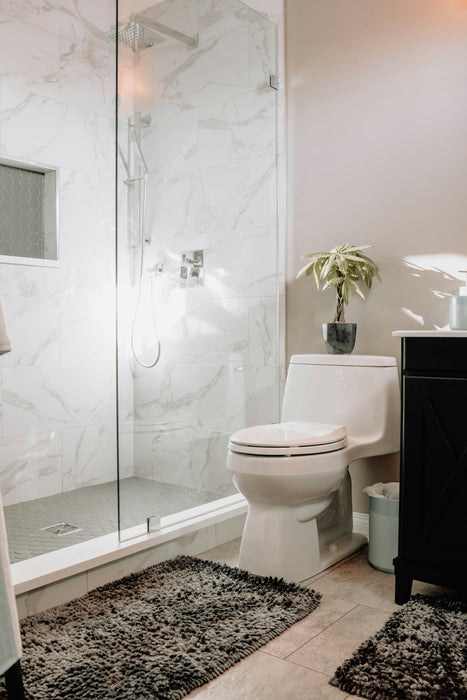
The bathroom is one of the most dangerous places for elderly individuals. Slippery floors, wet surfaces, and limited support structures make it a high-risk area for falls. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 80% of falls occur in the bathroom. A waterproof fall alert device ensures that seniors can wear or carry the device during showers or while performing other hygiene-related activities. Without waterproofing, seniors might remove the device, leaving them vulnerable during the moments when they are most at risk.
Ensuring Continuous Functionality
A waterproof fall alert device is more durable and resilient, capable of withstanding accidental spills, exposure to rain, or immersion in water. Devices that lack waterproofing can malfunction when exposed to moisture, potentially rendering them useless in emergencies. Continuous functionality is non-negotiable for a device designed to provide immediate assistance. By being waterproof, these devices maintain their reliability, even in unpredictable situations, ensuring that help is always just a button press or automatic alert away.
Promoting Daily Wearability
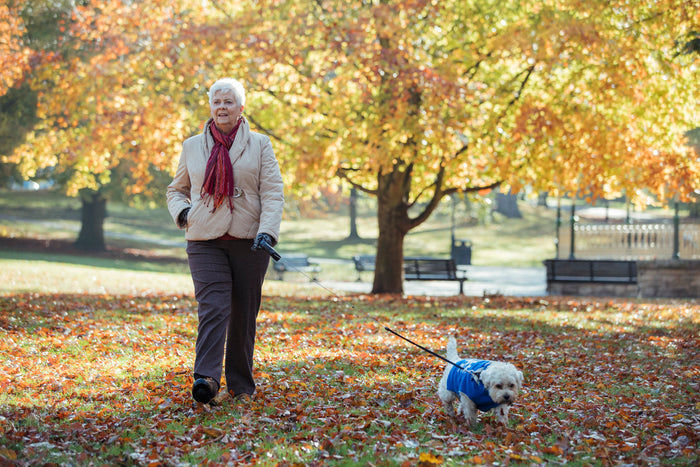
The elderly often forget or are reluctant to use assistive devices if they perceive them as cumbersome or unsuitable for daily activities. A waterproof design enhances the usability of fall alert devices by allowing seniors to wear them throughout the day without worry. Whether they are washing dishes, gardening in damp conditions, or enjoying water-based therapy, seniors can keep their fall alert device on without fear of damage. This consistent use increases the likelihood that the device will be available during an emergency.
Addressing Emotional Comfort
Waterproofing adds a layer of psychological comfort for both seniors and their caregivers. Seniors feel reassured knowing they are protected regardless of the environment, and their families can trust that the device will function properly when needed. This emotional security fosters independence while strengthening the bond of trust between caregivers and elderly individuals.
Enhancing Device Lifespan
Investing in a waterproof fall alert device often translates into long-term savings. These devices are better equipped to handle everyday wear and tear, reducing the likelihood of replacement or repair due to water-related damage. A longer lifespan not only ensures consistent safety but also provides greater value for families and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Waterproofing is a cornerstone feature of modern fall alert devices for seniors. It ensures safety in high-risk areas like bathrooms, promotes continuous functionality, and encourages daily wear, all while providing emotional comfort and extending device longevity. As we strive to improve the quality of life for the elderly, incorporating waterproof designs into fall alert devices is not just an added convenience—it’s a necessity. Families seeking to protect their loved ones should prioritise this feature, knowing it can make all the difference when seconds matter most. Go to WatchOvers.com for more information.